Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kakiuchi, Kazuo; Amaya, Masaki; Udagawa, Yutaka
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 171, p.109004_1 - 109004_9, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:76.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Tamura, Koji; Saeki, Morihisa
Kogaku, 48(1), p.13 - 20, 2019/01
By Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and by related resonance spectroscopy, elemental and isotope analysis of Uranium and Plutonium for nuclear fuel materials and in-situ remote analysis under strong radiation condition for melt downed nuclear fuel debris at damaged core in "Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station", are introduced and performed as one of the application in atomic energy research field.
 -irradiated graphite surfaces using photon-stimulated desorption spectroscopy
-irradiated graphite surfaces using photon-stimulated desorption spectroscopySekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao; Nath, K. G.
Surface and Interface Analysis, 38(4), p.352 - 356, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:7.13(Chemistry, Physical)We investigated the orientation nature at the top-most layers of F -irradiated graphite using polarization dependent near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) spectroscopy which incorporates partial electron yield (PEY) detection and photon-stimulated ion desorption (PSID) techniques. The fluorine K-edge NEXAFS spectra conducted in PEY mode show no significant dependence on polarization angles. In contrast, NEXAFS spectra recorded in F
-irradiated graphite using polarization dependent near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) spectroscopy which incorporates partial electron yield (PEY) detection and photon-stimulated ion desorption (PSID) techniques. The fluorine K-edge NEXAFS spectra conducted in PEY mode show no significant dependence on polarization angles. In contrast, NEXAFS spectra recorded in F ion yield mode show enhanced yields at a feature of
ion yield mode show enhanced yields at a feature of  689.4 eV assigned as a
689.4 eV assigned as a  *(C-F) state relevant to =C-F sites, which depend on polarization angles. The C-F bonds prefer relatively tilting down the surface at the top-most layer, while the C-F bonds are randomly directed at deeper regions. We conclude that the difference in the orientation structures between the top surface and bulk is reflected in the NEXAFS recorded in the two different detection modes. It was also found that H
*(C-F) state relevant to =C-F sites, which depend on polarization angles. The C-F bonds prefer relatively tilting down the surface at the top-most layer, while the C-F bonds are randomly directed at deeper regions. We conclude that the difference in the orientation structures between the top surface and bulk is reflected in the NEXAFS recorded in the two different detection modes. It was also found that H - and F
- and F - PSID NEXAFS spectra are helpful in understanding desorption mechanism, thus in analysing NEXAFS data.
- PSID NEXAFS spectra are helpful in understanding desorption mechanism, thus in analysing NEXAFS data.
Otani, Eiji*; Suzuki, Akio*; Ando, Ryota*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Advances in High-Pressure Technology for Geophysical Applications, p.195 - 209, 2005/09
This paper summarizes the techniques for the viscosity and density measurements of silicate melt and glasses at high pressure and temperature by using the X-ray radiography and absorption techniques in the third generation synchrotron radiation facility, SPring-8, Japan. The falling sphere method using in situ X-ray radiography makes it possible to measure the viscosity of silicate melts to the pressures above 6 GPa at high temperature. We summarize the details of the experimental technique of the viscosity measurement, and the results of the measurements of some silicate melts such as the albite and diopside-jadeite systems. X-ray absorption method is applied to measure the density of the silicate glasses such as the basaltic glass and iron sodium disilicate glass up to 5 GPa at high temperature. A diamond capsule, which is not reactive with the glass, is used for the density measurement of the glasses. The present density measurement of the glasses indicates that this method is useful for measurement of the density of silicate melts at high pressure and temperature.
 )
) SiX (X = F, Cl, Br, I, NCO) as studied using NEXAFS spectroscopy
SiX (X = F, Cl, Br, I, NCO) as studied using NEXAFS spectroscopySekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao; Nath, K. G.*; Uddin, M. N.*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 17(36), p.5453 - 5466, 2005/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.21(Physics, Condensed Matter)The orientation nature of multilayer organosilicon compounds has been investigated by measuring the dependence of the Si K-shell near-edge X-ray absorption fine structures (NEXAFS) on the polarization angle. Two approaches helped to elucidate the orientation mechanism: the substitution effect and the deposition-rate dependence. The orientation angles of Si-X bond axes were obtained for trimethylsilyl halides, (CH )
) SiX (X =F Cl Br I NCO, condensed on Cu(111) at a low (82 K) temperature: the angles are 60, 73, 61, 55, and 55 degrees with respect to the surface normal, for X =F, Cl, Br, I, and NCO, respectively. Chloride (X =Cl) produces the most parallel tilt angle. The specific orientation nature of chloride is attributed to its strong dipole moment as well as the regular tetrahedron shape of the molecule. The molecular volumes calculated verify this view. Furthermore, deposition rates are found to greatly influence the growth manner: namely, high deposition rates led to a slightly perpendicular orientation of Si-X bond axis.
SiX (X =F Cl Br I NCO, condensed on Cu(111) at a low (82 K) temperature: the angles are 60, 73, 61, 55, and 55 degrees with respect to the surface normal, for X =F, Cl, Br, I, and NCO, respectively. Chloride (X =Cl) produces the most parallel tilt angle. The specific orientation nature of chloride is attributed to its strong dipole moment as well as the regular tetrahedron shape of the molecule. The molecular volumes calculated verify this view. Furthermore, deposition rates are found to greatly influence the growth manner: namely, high deposition rates led to a slightly perpendicular orientation of Si-X bond axis.
 Sb
Sb Te
Te thin films; An X-ray absorption study
thin films; An X-ray absorption studyFons, P.*; Kolobov, A.*; Tominaga, Junji*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 238(1-4), p.160 - 162, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)Super-resolution (SR) media offer up to a factor of ten increase in areal storage density over conventional DVD media. Although SR has been realized, there is a strong need for a deeper understanding of structural and electronic changes in Ge Sb
Sb Te
Te (GST), a principal optical memory component, with external perturbations. Recording of SR disks leads to the formation of gas-phase bubbles that in turn lead to the development of large stresses on the underlying GST layer. In this paper we report on XAFS of nominally hydrostatic (0-10 GPa) compressive stress-induced structural changes of the metastable crystalline phase of GST. An analysis showed that the initial splitting of Ge Te bond lengths of the room-temperature distorted rocksalt structure decreased to a small but finite splitting for
(GST), a principal optical memory component, with external perturbations. Recording of SR disks leads to the formation of gas-phase bubbles that in turn lead to the development of large stresses on the underlying GST layer. In this paper we report on XAFS of nominally hydrostatic (0-10 GPa) compressive stress-induced structural changes of the metastable crystalline phase of GST. An analysis showed that the initial splitting of Ge Te bond lengths of the room-temperature distorted rocksalt structure decreased to a small but finite splitting for 
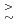 6 GPa. The implications of this upon the proposed ferroelectric catastrophe super-RENS readout mechanism are discussed.
6 GPa. The implications of this upon the proposed ferroelectric catastrophe super-RENS readout mechanism are discussed.
Nath, K. G.; Shimoyama, Iwao; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji
Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 144-147, p.323 - 326, 2005/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:27.33(Spectroscopy)The effect of laser annealing on electronic atructures and molecular orientation for poly(dimethylsilane), {PDMS, [Si(CH )
) ]
] } has been studied by synchrotron radiation photoemission and photoabsorption spectroscopy. Prior to annealing, PDMS powder was mounted on the basal plane of highly oriented pyrolytic graphite. Both Si 1s X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) spectroscopy at Si 1s edge show that electronic structures have been modified due to annealing. Furthermore, the angle-dependent NEXAFS spectra clearly indicate that the annealed products maintain a specific orientation. Interestingly, no such kind of orientation is present in as-received PDMS powder as no angle-dependency is observed before annealing.
} has been studied by synchrotron radiation photoemission and photoabsorption spectroscopy. Prior to annealing, PDMS powder was mounted on the basal plane of highly oriented pyrolytic graphite. Both Si 1s X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) spectroscopy at Si 1s edge show that electronic structures have been modified due to annealing. Furthermore, the angle-dependent NEXAFS spectra clearly indicate that the annealed products maintain a specific orientation. Interestingly, no such kind of orientation is present in as-received PDMS powder as no angle-dependency is observed before annealing.
Konishi, Hiroyuki; Yamashita, Masato*; Uchida, Hitoshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Materials Transactions, 46(2), p.329 - 336, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:80.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Chloride in atmosphere considerably reduces the corrosion resistance of conventional weathering steel containing a small amount of Cr. Ni is an effective anticorrosive element for improving the corrosion resistance of steel in a Cl-rich environment. In order to clarify the structure of the protective rust layer of weathering steel, Cl and Fe K-edge X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectra of atmospheric corrosion products (rust) formed on Fe, Fe-Ni and Fe-Cr alloys exposed to Cl-rich atmosphere were measured. The Fe K-XANES measurements enable the characterization of a mixture of iron oxides such as rust. The chemical composition of the rust was determined by performing pattern fitting of the measured spectra. All the rust is composed mainly of goethite, akagan ite, lepidocrocite and magnetite. Among these iron oxides, akagan
ite, lepidocrocite and magnetite. Among these iron oxides, akagan ite in particular is the major component in the rust. Additionally, the amount of akagan
ite in particular is the major component in the rust. Additionally, the amount of akagan ite in the rust of Fe-Ni alloy is much greater than that in rust of Fe-Cr alloy. Akagan
ite in the rust of Fe-Ni alloy is much greater than that in rust of Fe-Cr alloy. Akagan ite is generally considered to facilitate the corrosion of steel, but our results indicate that akagan
ite is generally considered to facilitate the corrosion of steel, but our results indicate that akagan ite in the rust of Fe-Ni alloy is quantitatively different from that in rust of Fe-Cr alloy and does not facilitate the corrosion of steel. The shoulder peak observed in Cl K-XANES spectra reveals that the rust contains a chloride other than akagan
ite in the rust of Fe-Ni alloy is quantitatively different from that in rust of Fe-Cr alloy and does not facilitate the corrosion of steel. The shoulder peak observed in Cl K-XANES spectra reveals that the rust contains a chloride other than akagan ite. The energy of the shoulder peak does not correspond to that of any well-known chlorides. In the measured spectra, there is no proof that Cl, by combining with the alloying element, inhibits the alloying element from acting in corrosion resistance. The shoulder peak appears only when the content of the alloying element is lower than a certain value. This suggests that the generation of the unidentified chloride is related to the corrosion rate of steel.
ite. The energy of the shoulder peak does not correspond to that of any well-known chlorides. In the measured spectra, there is no proof that Cl, by combining with the alloying element, inhibits the alloying element from acting in corrosion resistance. The shoulder peak appears only when the content of the alloying element is lower than a certain value. This suggests that the generation of the unidentified chloride is related to the corrosion rate of steel.
Konishi, Hiroyuki; Yamashita, Masato*; Uchida, Hitoshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Materials Transactions, 45(12), p.3356 - 3359, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:53.05(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Cl K-edge XANES measurements of atmospheric corrosion products (rust) formed on Fe, Fe-Ni and Fe-Cr alloys in chloride pollution have been performed using synchrotron radiation in order to clarify roles of anticorrosive alloying elements and of Cl in the corrosion resistance of weathering steel. The spectra of binary alloys show a shoulder structure near the absorption edge. The intensity of the shoulder peak depends on the kind and amount of the alloying element, whereas the energy position is invariant. This indicates that Cl is not combined directly with alloying elements in the rust.
Yokoya, Akinari; Takakura, Kaoru*; Watanabe, Ritsuko; Akamatsu, Ken*; Ito, Takashi*
Radiation Research, 162(4), p.469 - 473, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:10.06(Biology)X-ray absorption spectra from single crystals of 5-Bromouracil were measured with the transmission mode in the energy range from 13.41 to 13.50 keV using the linearly polarized synchrotron radiation (SR). A characteristic resonance structure, consisting of four peaks, was recognized in the spectra in the Br K-edge region. The intensities of these peaks were strongly dependent on the crystal rotation about the normal of the crystal b-c plane, which was set perpendicular to the X-ray beam direction. (SR X-rays are polarized in the horizontal plane.) Molecular orbital calculations indicate that these resonance peaks are associated with the transitions from the 1s electron of Br to the Br-C molecular antibonding orbitals and to a shape resonance. The observed anisotropy of each photoabsorption peak might originate from the angular dependences of these molecular orbitals.
Muramatsu, Yasuji; Motoyama, Muneyuki*; Denlinger, J. D.*; Gullikson, E. M.*; Perera, R. C. C.*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 42(10), p.6551 - 6555, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:28.14(Physics, Applied)Carbon films on Japanese smoked roof tile "Ibushi-Kawara" were characterized by high-resolution soft X-ray spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation. By comparing the soft X-ray emission and absorption spectra of Kawara with the reference carbon compounds, it was determined that the carbon films on Kawara consist of mostly carbon-black-like sp2 carbon atoms and that the surface also contains polyethylene-like sp3 carbon atoms. The take-off/incident-angle dependence on the X-ray emission/absorption spectra of Kawara implies that the carbon-black-like sp2 carbon atoms partially form a layer structure parallel to the basal clay plane. From the take-off-angle dependence of the p/s-peak intensity ratio in the X-ray emission spectra, the layer ordering of the carbon films is estimated to be 50% of highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG). Therefore, the metallic oxidized color and durability are due to the layer structure and the random structure that connects the layer-structured clusters, respectively.
Sakaba, Nariaki; Nakazawa, Toshio; Kawasaki, Kozo; Urakami, Masao*; Saishu, Sadanori*
JAERI-Research 2003-006, 65 Pages, 2003/03
In the final third stage of the research and development for a high-temperature helium-leak detection system, the radiation sensor was developed in order to detect very small helium leakage. Applying the radiation sensor, we proposed not only the direct detection method which uses the detection of FP gas in helium, but also the active method which uses the difference in the radiation absorption between helium and air. From obtained data it was found that we can detect 0.2 cm /s leakage within 10 minutes by the active method.
/s leakage within 10 minutes by the active method.
Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao
Surface Review and Letters, 9(1), p.77 - 83, 2002/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:26.08(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Usami, Noriko*; Yokoya, Akinari; Ishizaka, Shozo*; Kobayashi, Katsumi*
Journal of Radiation Research, 42(3), p.317 - 331, 2001/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:28.35(Biology)The characteristics of DNA lesions produced by the phosphorus K-shell absorption in yeast cells were studied using monochromatized soft X-rays tuned to the phosphorus K-edge peak (2153 eV) and below the peak energy (2147 eV). The repaired fractions of DNA double-strand breaks (dsb) were measured relatively by using both a mutant, (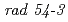 ), which shows the temperature-sensitive dsb repair-deficient, and a wild-type strain. The repaired fraction of lesion in
), which shows the temperature-sensitive dsb repair-deficient, and a wild-type strain. The repaired fraction of lesion in 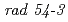 , which corresponds to the relative yield of dsb reparable by the
, which corresponds to the relative yield of dsb reparable by the 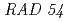 pathway, was not affected by the phosphorus photoabsorption. Repair of the produced lesions in the wild-type cells was also measured by comparing the surviving fraction of the immediately plated cells to that of those cells plated after holding in a non-nutrient medium for 80 hrs. The recovery of the surviving fraction after the holding treatment was dependent upon the soft X-ray energy. These results suggest that irrepairable lesions are produced by the inner-shell photoabsorption of phosphorus in DNA, although its yield is small.
pathway, was not affected by the phosphorus photoabsorption. Repair of the produced lesions in the wild-type cells was also measured by comparing the surviving fraction of the immediately plated cells to that of those cells plated after holding in a non-nutrient medium for 80 hrs. The recovery of the surviving fraction after the holding treatment was dependent upon the soft X-ray energy. These results suggest that irrepairable lesions are produced by the inner-shell photoabsorption of phosphorus in DNA, although its yield is small.
*; Kawanishi, Shunichi; Nishii, Masanobu; Sugimoto, Shunichi*; *
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 33(8), p.4764 - 4768, 1994/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:50.63(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
 at the Si 1s edge
at the Si 1s edgeBaba, Yuji; Sasaki, Teikichi; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki
Physical Review B, 49(1), p.709 - 711, 1994/01
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:86.42(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Baba, Yuji; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Sasaki, Teikichi
Surface Science, 307-309, p.896 - 900, 1994/00
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:83.34(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 (0
(0 x
x 2) and SiN
2) and SiN (0
(0 x
x 4/3) produced by low-energy ion implantation in Si(100)
4/3) produced by low-energy ion implantation in Si(100)Baba, Yuji; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Sasaki, Teikichi
Physical Review B, 48(15), p.10972 - 10977, 1993/10
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:77.19(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 single crystals after gamma-ray irradiation
single crystals after gamma-ray irradiation;
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 3, p.126 - 127, 1964/00
no abstracts in English